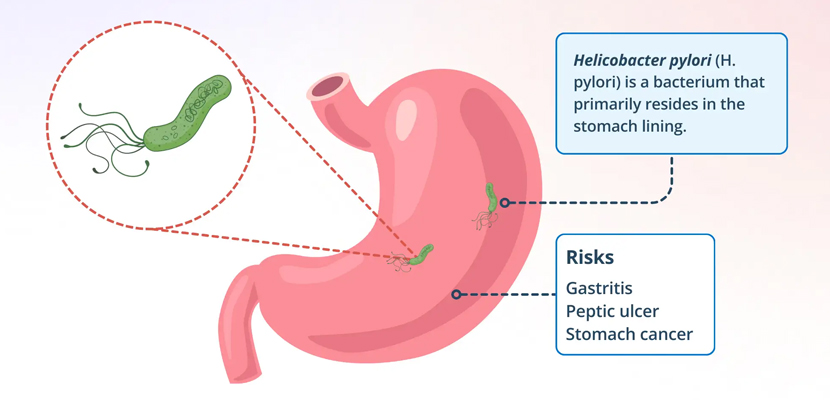
H.pylori Testing
Upper GI (gastrointestinal) endoscopy, also known as esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), is a diagnostic procedure used to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. It is commonly performed to evaluate symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or unexplained weight loss. A common diagnostic application of upper GI endoscopy is testing for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), a bacteria linked to gastritis, peptic ulcers, and gastric cancer.
Symptoms Suggestive of H. pylori Infection
- Persistent upper abdominal pain or discomfort
- Bloating or a feeling of fullness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Frequent burping or acid reflux
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
Causes of H. pylori Infection
- Contaminated food or water: Consumption of improperly prepared or unclean food and beverages.
- Person-to-person contact: Close contact, such as sharing utensils or exposure to saliva, can spread the bacteria.
- Poor hygiene: Inadequate sanitation practices increase the risk of transmission.
Treatment
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): Omeprazole or lansoprazole reduce stomach acid, improving healing.
- Antibiotics: Combination therapy with two antibiotics (e.g., amoxicillin, clarithromycin, or metronidazole) eradicates the bacteria.
- Bismuth-containing agents: In some regimens, bismuth subsalicylate is added to enhance efficacy.