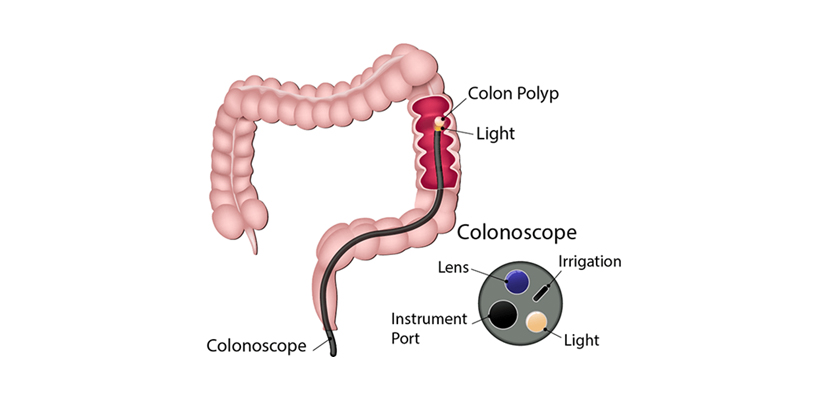
Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure that involves using a flexible tube with a camera (sigmoidoscope) to examine the lower part of the colon, known as the sigmoid colon, and the rectum. It is commonly used to investigate symptoms like rectal bleeding, unexplained abdominal pain, or changes in bowel habits, and to screen for colorectal cancer in individuals at average risk.
Indications for Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy is recommended for:
- Screening for Colorectal Cancer: Particularly in individuals with a family history or those above the age of 50.
- Evaluating Lower GI Symptoms: Such as rectal bleeding, persistent diarrhea, constipation, or unexplained abdominal pain.
- Surveillance of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Monitoring disease activity in conditions like ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease.
- Detection of Polyps or Cancer: Identifying precancerous polyps, tumors, or other abnormalities in the sigmoid colon and rectum.
Treatment during Sigmoidoscopy
- Polypectomy: Removal of polyps that are found during the procedure. This is often done with a snare or forceps, and can prevent progression to cancer.
- Biopsy: Small tissue samples may be taken for further examination, especially if suspicious lesions or signs of cancer or inflammation are observed.
- Hemostasis: If bleeding is encountered, techniques such as injection therapy (epinephrine) or cauterization can be used to stop the bleeding.
- Dilation: In cases of narrowing or strictures (e.g., from Crohn’s disease), a balloon may be used to gently expand the area.
Post-Procedure Care
- Patients typically experience mild discomfort or bloating after the procedure, which usually resolves quickly.
- Normal activities can generally be resumed after a short recovery period, although patients should avoid heavy meals and strenuous activities initially.