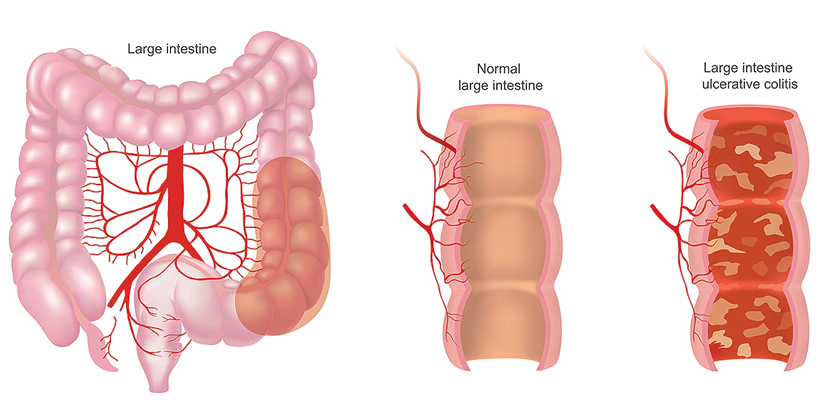
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative Colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes long-term inflammation and ulcers (sores) in the innermost lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum. The condition can affect individuals at any age but commonly develops between the ages of 15 and 30.
Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis:
The symptoms of UC vary in severity and may come and go in flare-ups. Common symptoms include:
- Diarrhea: Often with blood or mucus, due to ulceration in the colon.
- Abdominal pain and cramping: Often relieved after a bowel movement.
- Rectal bleeding: This occurs because of ulcers that bleed in the colon.
- Urgency to have a bowel movement: A feeling of incomplete evacuation.
- Fatigue: Due to anemia (from blood loss) and inflammation.
- Weight loss: Often associated with malabsorption of nutrients.
- Fever: This may occur during flare-ups or severe disease.
Causes of Ulcerative Colitis:
The exact cause of UC remains unclear, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
- Immune system dysfunction: UC is thought to result from an abnormal immune response where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the colon, causing inflammation.
- Genetics: A family history of UC or other inflammatory bowel diseases increases the risk. Certain genetic mutations are linked to the condition.
- Environmental factors: Diet, stress, and other environmental triggers may exacerbate the disease. While these factors do not cause UC, they can contribute to flare-ups.
Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis:
There is no cure for UC, but various treatments can help manage symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve quality of life. Treatment options include:
Medications:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., aminosalicylates) help reduce inflammation in the colon.
- Immunosuppressive drugs (e.g., corticosteroids) suppress the immune system's abnormal activity.
- Biologic therapies: These target specific components of the immune system and are used for moderate to severe UC.
- Antibiotics: Used to treat infections if they occur due to the disease.
Surgery: In severe cases or when medications fail, surgery may be necessary. The most common procedure is colectomy, which involves removing the colon and rectum. A permanent ileostomy or ileoanal anastomosis may be performed, depending on the patient’s needs.