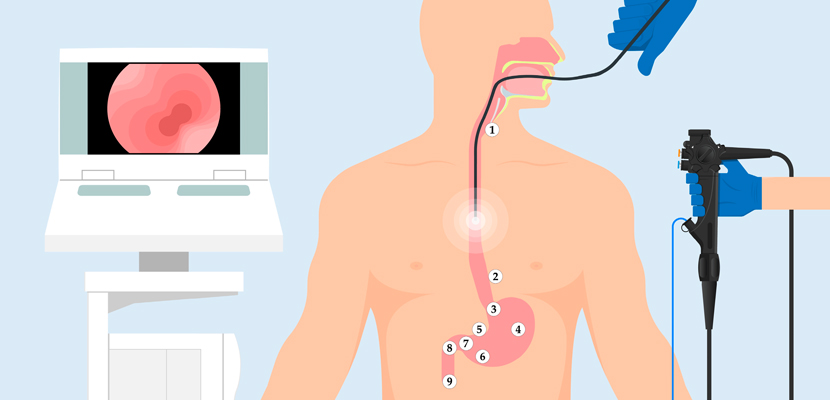
Upper GI Endoscopy Diagnostic
Upper GI endoscopy, also known as esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), is a diagnostic procedure used to examine the upper part of the digestive tract, including the esophagus, stomach, and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). It is performed using a thin, flexible tube called an endoscope equipped with a light and camera, allowing for direct visualization and evaluation of the gastrointestinal (GI) lining.
Symptoms
- Persistent heartburn or acid reflux.
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
- Unexplained nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain.
- Blood in vomit or stools (melena).
- Unexplained weight loss.
Suspected Conditions:
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD).
- Peptic ulcers.
- Esophagitis or gastritis (inflammation).
- Hiatal hernia.
- Celiac disease.
- Tumors or cancers in the upper GI tract.
- Barrett's esophagus (pre-cancerous changes in the esophagus).