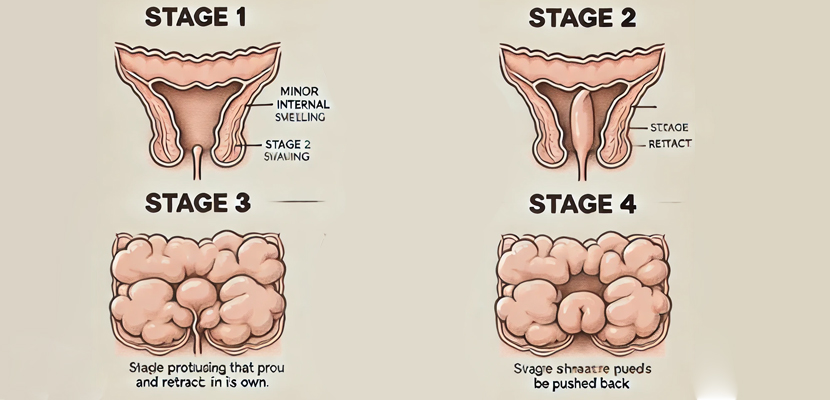
Piles
Piles, or hemorrhoids, are swollen and inflamed veins in the rectum and anus. They can cause discomfort, bleeding, and irritation. Piles are common and can affect people of all ages, but are more frequent in adults, particularly those over 45.
Symptoms
Piles can be internal (inside the rectum) or external (under the skin around the anus). Symptoms vary based on their type and severity:
Internal Piles:
- Painless bleeding during bowel movements, often noticed as bright red blood in the stool or toilet.
- Protrusion or prolapse of tissue through the anus, which may recede on its own or require manual assistance.
External Piles:
- Pain or discomfort, especially while sitting.
- Swelling or a lump near the anus.
- Itching, irritation, or inflammation around the anus.
- Bleeding, particularly if the piles rupture.
Thrombosed Piles:
- Severe pain due to a blood clot in the pile.
- Bluish or purplish discoloration of the lump.
Causes
Piles result from increased pressure in the lower rectum, which leads to swollen veins. Contributing factors include:
- Chronic Constipation or Straining: Hard stools increase pressure during bowel movements.
- Prolonged Sitting: Especially on the toilet, which strains rectal veins.
- Low-Fiber Diet: Affects digestion and stool consistency.
- Obesity: Adds pressure on pelvic veins.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased abdominal pressure can lead to piles.
- Aging: Weakens rectal and anal vein walls over time.
- Heavy Lifting: Frequent strain increases the risk.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of piles may make some more susceptible.
Treatment
Treatment depends on severity and symptoms:
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Increase fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Drink plenty of water to soften stools.
- Exercise regularly to prevent constipation.
- Avoid prolonged sitting or straining during bowel movements.
Medications:
- Over-the-counter creams, ointments, and suppositories to reduce pain, swelling, and itching.
- Stool softeners or laxatives for easier bowel movements.
Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Rubber Band Ligation: A band is placed around the pile to cut off its blood supply.
- Sclerotherapy: Injection of a solution to shrink piles.
- Coagulation Therapy: Use of infrared or laser light to shrink tissue.
Surgical Treatments:
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Removal of large, severe piles.
- Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: Minimally invasive surgery to reposition and shrink piles.