Hepatitis
Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver, a vital organ responsible for detoxification, digestion, and metabolism. This condition can result from various causes, including infections, autoimmune disorders, or toxic substances, and may range in severity from mild to life-threatening.
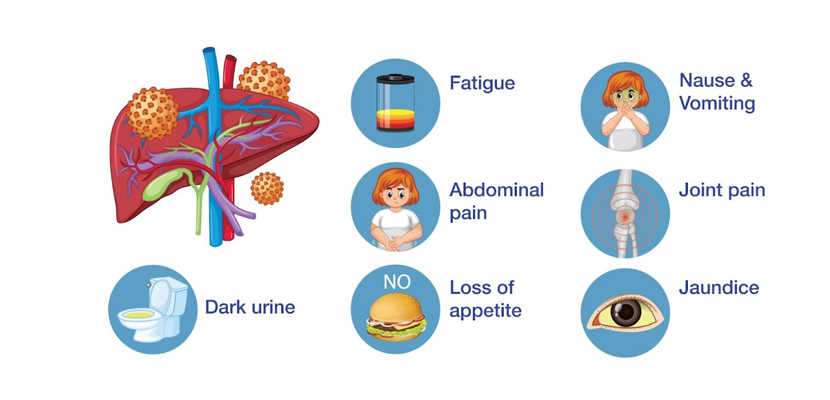
Symptoms
Hepatitis often presents with a range of symptoms, some of which may overlap with other illnesses. These include:
- General symptoms: Fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting.
- Specific liver-related symptoms: Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), dark urine, pale stools, and abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right quadrant.
- Chronic hepatitis: Persistent inflammation can lead to liver scarring (fibrosis), cirrhosis, or liver failure, often manifesting as swelling in the abdomen, confusion, or easy bruising.
Causes
Hepatitis can be caused by multiple factors:
Viral infections:
- Hepatitis A (HAV): Transmitted through contaminated food or water, often self-limiting.
- Hepatitis B (HBV) and Hepatitis C (HCV): Spread through blood, sexual contact, or from mother to child. These can progress to chronic liver disease.
- Hepatitis D (HDV): Requires HBV infection to replicate, exacerbating disease severity.
- Hepatitis E (HEV): Spread via contaminated water, more severe in pregnant women.
Alcohol and toxins: Excessive alcohol consumption or exposure to drugs and industrial chemicals can damage liver cells.
Autoimmune hepatitis: The immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type and severity of hepatitis:
Acute viral hepatitis:
- HAV and HEV: Usually resolve on their own with supportive care such as hydration and rest.
- HBV and HCV: Acute cases may require monitoring for progression.
Chronic hepatitis:
- HBV: Antiviral medications like entecavir or tenofovir can suppress viral replication.
- HCV: Direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) like sofosbuvir can achieve high cure rates.
Non-infectious causes:
- Alcoholic hepatitis: Abstinence and nutritional support are essential.
- Autoimmune hepatitis: Immunosuppressive drugs like corticosteroids are prescribed.
Advanced cases: Cirrhosis or liver failure may necessitate liver transplantation.