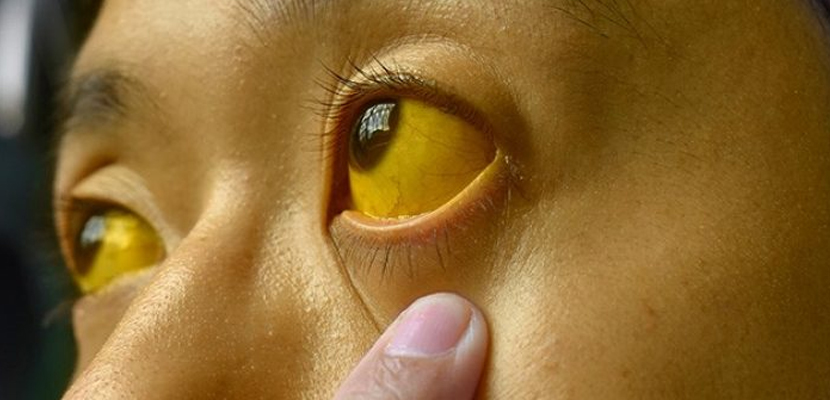
Jaundice
Jaundice is a condition characterized by the yellowing of the skin, whites of the eyes, and mucous membranes due to an elevated level of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment formed by the breakdown of red blood cells. It is processed by the liver and excreted in bile. Jaundice itself is not a disease but a symptom of underlying conditions.
Symptoms
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes: This is the hallmark sign of jaundice.
- Dark-colored urine: Excess bilirubin in the bloodstream can darken the color of urine.
- Pale or clay-colored stools: Blockage in bile flow can lead to light-colored stools.
- Itching: Accumulation of bile salts in the skin can cause itchiness.
- Fatigue and weakness: These may accompany jaundice, depending on the underlying cause.
- Abdominal pain: Particularly in cases associated with liver or gallbladder disease.
Causes
Jaundice can result from issues in different stages of bilirubin metabolism:
Pre-hepatic (before the liver):
- Excessive breakdown of red blood cells (e.g., hemolytic anemia).
- Conditions like sickle cell anemia or malaria.
Hepatic (within the liver):
- Liver diseases such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
- Genetic disorders like Gilbert’s syndrome.
Post-hepatic (after the liver):
- Blockage of bile ducts due to gallstones, tumors, or strictures.
- Pancreatic cancer affecting bile flow.
Treatment
Treatment for jaundice depends on addressing the underlying cause:
For pre-hepatic causes:
- Management involves treating the condition causing excessive red blood cell breakdown, such as anemia or infections.
For hepatic causes:
- Hepatitis: Antiviral or steroid medications.
- Cirrhosis: Lifestyle changes, avoiding alcohol, and medications to manage complications.
- In severe cases, a liver transplant may be required.
For post-hepatic causes:
- Gallstones: Surgery or endoscopic removal.
- Tumors: Surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.