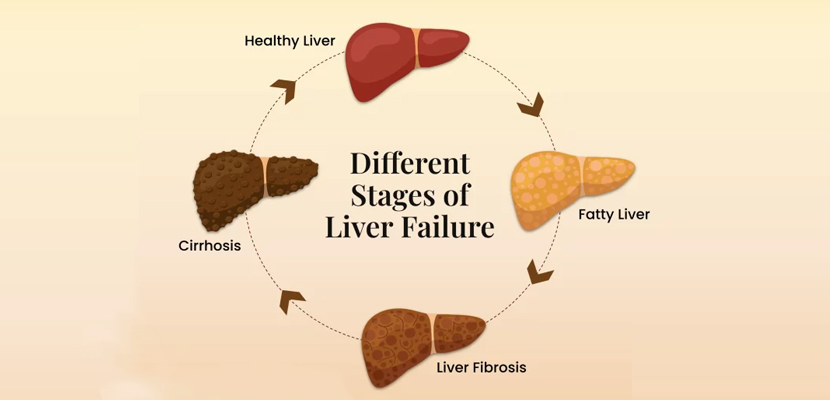
Liver Diseases
The liver is a vital organ responsible for detoxification, metabolism, and nutrient storage. Liver diseases encompass a wide range of conditions that impair its normal functions, potentially leading to serious health complications.
Symptoms of Liver Diseases
The symptoms of liver diseases vary depending on the specific condition but often include:
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness is a common early symptom.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to elevated bilirubin levels.
- Abdominal Pain and Swelling: Pain in the upper right abdomen and fluid buildup (ascites).
- Nausea and Vomiting: Common due to impaired digestion and detoxification.
- Dark Urine and Pale Stools: Result from altered bile processing.
- Swelling in Legs and Ankles: Linked to fluid retention.
- Unexplained Weight Loss or Gain: May indicate underlying liver issues.
- Itchy Skin: Caused by bile accumulation in the bloodstream.
Causes of Liver Diseases
Liver diseases can arise from various factors, including:
- Infections: Hepatitis A, B, C, and E caused by viruses are common culprits.
- Alcohol Abuse: Chronic alcohol consumption leads to alcoholic liver disease and cirrhosis.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Caused by obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like autoimmune hepatitis attack liver cells.
- Genetic Conditions: Disorders like Wilson's disease and hemochromatosis affect liver function.
- Drug Toxicity: Overuse of medications like acetaminophen can damage the liver.
- Cancer: Primary liver cancers, such as hepatocellular carcinoma, or metastases from other sites.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type and severity of liver disease:
- Lifestyle Changes: For mild conditions like fatty liver, weight loss, healthy diet, regular exercise, and alcohol cessation are crucial.
- Medications: Antiviral drugs treat hepatitis infections, while steroids manage autoimmune liver diseases.
- Surgical Interventions: In severe cases, like tumors or advanced liver damage, surgical resection or liver transplant may be necessary.
- Management of Complications: Diuretics for fluid retention, lactulose for hepatic encephalopathy, and vitamin supplements.
- Regular Monitoring: For chronic liver diseases, frequent check-ups and liver function tests (LFTs) are essential.